Dercum’s Disease: Understanding Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
Dercum’s disease, also known as adiposis dolorosa, is a rare and poorly understood condition characterized by painful fatty tumors, or lipomas, typically found on the arms, legs, and trunk. While the exact cause remains unknown, research suggests a possible link to nerve damage and hormonal imbalances. This comprehensive guide explores the various aspects of Dercum’s disease, providing information on its symptoms, diagnostic processes, available treatment options, and ongoing research efforts.
Understanding the Symptoms of Dercum’s Disease
The hallmark symptom of Dercum’s disease is the presence of multiple, painful lipomas. These lipomas can vary significantly in size and location, and their pain level can fluctuate. The pain associated with these lipomas is often described as intense, burning, aching, or shooting, and it can be exacerbated by touch, pressure, or changes in temperature. The pain can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, leading to difficulties with sleep, mobility, and daily activities.
Beyond the painful lipomas, other symptoms associated with Dercum’s disease include:

- Fatigue and weakness
- Joint pain and stiffness
- Headaches
- Numbness or tingling in the extremities
- Cognitive difficulties, such as memory problems or brain fog
- Depression and anxiety
- Sleep disturbances
- Weight gain or difficulty losing weight
The severity of symptoms can vary greatly from person to person. Some individuals may experience mild discomfort, while others may face debilitating pain and significant limitations in their daily routines. It’s crucial to remember that these symptoms can overlap with other conditions, making accurate diagnosis challenging.

Diagnosing Dercum’s Disease: A Complex Process
Diagnosing Dercum’s disease can be a lengthy and complex process, often involving ruling out other conditions with similar symptoms. There is no single definitive test for Dercum’s disease, and diagnosis is typically based on a combination of factors:
- Physical examination: A thorough physical examination by a physician is crucial, focusing on the location, size, and consistency of the lipomas, as well as assessing overall pain levels and other reported symptoms.
- Medical history: A detailed medical history, including a review of past illnesses, medications, and family history, can provide valuable clues.
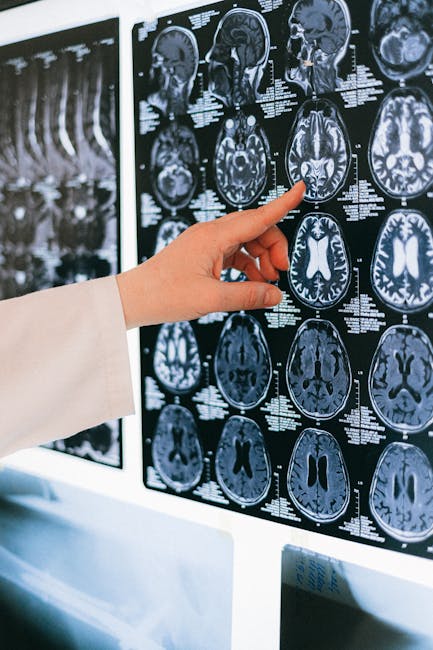
- Imaging tests: Imaging studies such as ultrasound, MRI, or CT scans can help confirm the presence of lipomas and rule out other possible causes of pain or swelling.
- Blood tests: Blood tests may be conducted to assess hormone levels, rule out other medical conditions, and evaluate overall health.
- Biopsy: In some cases, a biopsy of a lipoma may be performed to exclude other possibilities, though this is not routinely used for diagnosis.
The diagnostic process often requires collaboration between multiple specialists, including pain management specialists, endocrinologists, and rheumatologists. The lack of a definitive diagnostic test and the overlapping symptoms with other conditions often lead to delays in diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Dercum’s Disease
Currently, there is no cure for Dercum’s disease. Treatment focuses primarily on managing symptoms and improving the patient’s quality of life. Options may include:
Pain Management Strategies:
- Medications: Pain relievers (analgesics), such as NSAIDs or opioids, may be prescribed to manage pain. Antidepressants and anticonvulsants can sometimes help alleviate neuropathic pain.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help improve mobility, strength, and range of motion, reducing pain and improving functionality.
- Occupational therapy: Occupational therapy can assist in adapting daily activities to manage pain and improve overall independence.
- Alternative therapies: Some individuals find relief through alternative therapies such as acupuncture, massage, or heat/cold therapy.
Surgical Options:
Liposuction is sometimes considered to remove lipomas, but this may not address the underlying pain and may lead to the development of new lipomas.
Other Treatments:
- Hormone therapy: In some cases, hormone replacement or modulation may be explored to see if it alleviates symptoms, though this is often not a reliable option.
- Weight management: While not directly addressing the root cause, weight management can help reduce overall discomfort.
Ongoing Research and Future Directions
Research into Dercum’s disease is ongoing, with scientists working to understand the underlying causes of the condition and develop more effective treatments. Researchers are exploring potential genetic factors, hormonal imbalances, and the role of the nervous system in the development and progression of Dercum’s disease. Clinical trials are underway to evaluate new therapeutic approaches, and increased awareness and collaboration among researchers are crucial for advancing our understanding and improving outcomes for individuals affected by this rare condition.
Living with Dercum’s Disease: Coping Strategies and Support
Living with Dercum’s disease can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. Developing coping strategies and seeking support from others is crucial. Joining support groups, connecting with other individuals who understand the condition, and seeking psychological support can significantly aid in managing the emotional burden of the disease. Open communication with healthcare providers, family, and friends is also essential for obtaining appropriate care and maintaining a strong support network.
In conclusion, Dercum’s disease is a complex and debilitating condition that requires a multidisciplinary approach to diagnosis and management. While there is no cure, ongoing research and advancements in treatment options offer hope for the future. Individuals affected by Dercum’s disease can find support and empowerment by actively participating in their healthcare, fostering strong relationships, and advocating for increased research and awareness.
